Control plane connections: A control plane connection is established between each Cisco vSmart Controller with each edge router in the overlay network. Each control plane connection (which runs as a DTLS tunnel), is established after device authentication is complete, and carries the encrypted payload. This payload consists of route information, required for the Cisco vSmart Controller to determine the network topology, and calculate the best routes and distribute this route information to the Edge routers.
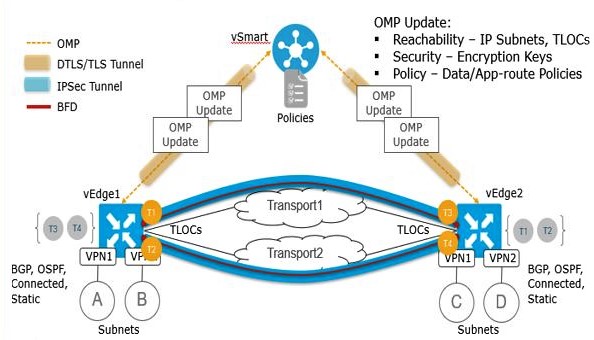
OMP (Overlay Management Protocol): The OMP is a routing protocol that manages the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network. OMP carries the routes, next hops, keys, and policy information and runs inside the DTLS control plane connections to establish and maintain the overlay network. OMP carries only control plane information and exists between the Cisco vSmart Controller and the edge routers. The Cisco vSmart Controller receives the routes and advertises reachability information to other edge routers in the overlay network.
Authentication: The Cisco vSmart Controller authenticates every new edge router using pre-installed credentials. These credentials allow access only authenticated devices to the network.
Key reflection and rekeying: The Cisco vSmart Controller receives data plane keys from the the edge router and reflects the same to other edge routers that will send data plane traffic.
Policy engine: The Cisco vSmart Controller manipulates routing information, access control, segmentation, etc. with its rich inbound and outbound policy constructs
Netconf: Cisco vManage uses Netconf to provision Cisco vSmart Controller. The Cisco vSmart Controller maintains a centralized route table that stores all the OMP routes, which it learns from the edge routers and from other Cisco vSmart Controllers in the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network. The Cisco vSmart Controller shares these OMP routes with the edge routers so that they can communicate with each other.
Single root-of-trust public certificate: A single root-of-trust public certificate is embedded into the Cisco SD-WAN vSmart software image. We need to perform minimal configuration, such as the IP addresses of the vSmart and the vBond Orchestrator during the initial startup of a Cisco vSmart Controller. Cisco vSmart Controller authenticates itself on the network, and establishes a DTLS control connection with the Cisco vBond Orchestrator, and receives its full configuration from Cisco vManage for activation. The Cisco vSmart Controller has become ready to accept connections from the edge routers.
Redundancy and high availability: Multiple Cisco vSmart Controllers should be present in each domain (maximum 20) for redundancy and high availability. All the Cisco vSmart Controllers in a domain should have the same policy and OMP configuration to synchronize OMP routes. But, device-specific information configuration, such as interface addresses, system ID, hostname etc., may be different. In a network with redundant Cisco vSmart Controllers, the vBond Orchestrator informs the vSmart Controller about other Controllers and instructs each vSmart Controller regarding the acceptance of control connections from specific edge routers in the domain. Any edge router may be connected to different Cisco vSmart Controllers for load balancing. If any vSmart Controller becomes unavailable, then the other controllers in the domain become available automatically to sustain the functioning of the overlay network.