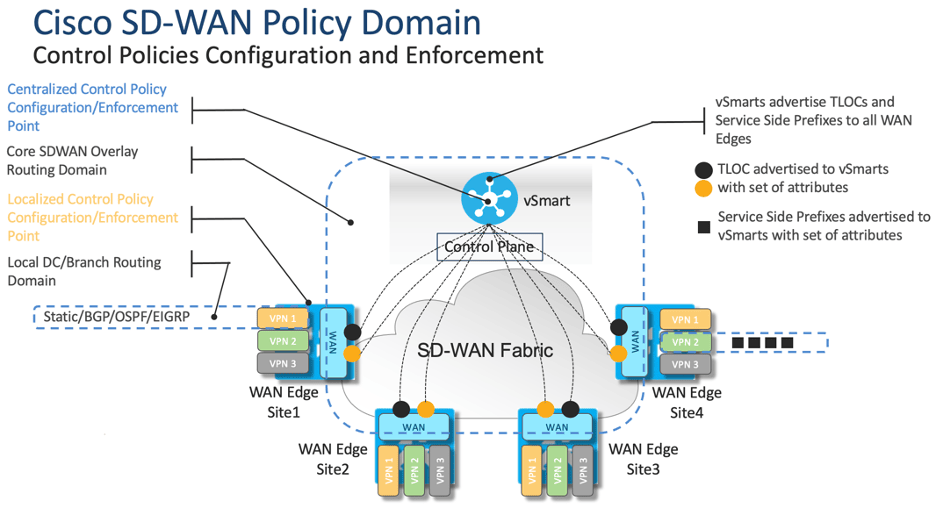
Cisco SD-WAN Policies are used to control the flow of data traffic among the WAN Edge routers in the overlay network. Control plane or Data plane traffic are controlled by the policy and configured on vSmart controllers (centralized policy) or WAN Edge routers (localized policy).
Centralized control policies are based on the routing and TLOC information and controls routing decisions and routing paths through the overlay network. Traffic engineering, service insertion, and VPN topologies (full-mesh, hub-and-spoke etc.) can be configured using these policies.
Application-aware routing is an important centralized control policy, which is used to select the optimal path based on real-time path performance for different types of traffic. Routing policy at a local site is affected by Localized control policies, using OSPF or BGP route maps and prefix lists.
Data policies impact the data traffic flow based on the IP packet headers and VPN membership. Application firewalls, Service chaining, TE, QoS and Cflowd are configured using Centralized data policies. How data traffic is handled at a specific site, such as ACLs, QoS etc. are configured using Localized data policies. In few cases, Centralized data policy may affect the WAN Edge, as in the case of app-route policies or QoS classification policy. In these cases, the configuration is still downloaded directly to the vSmart controllers, but any policy information that needs to be conveyed to the WAN Edge routers is communicated through OMP.
Configuring Localized Policy
Localized policy is configured and applied in three steps:
Localized policy is created in vManage under Configuration -> Policies and then select the Localized Policy tab. Under the Additional Templates section next to Policy in the device template, the name of the localized policy is referenced.
When a device template includes a feature template (which already has a route policy or prefix list or any other localized policy), policy name must be referenced while creating or updating the device template. If a device is attached to an existing device template, a localized policy to be attached first to the device template before referring any localized policy elements within all the feature templates those are part of that device template.
Only one localized policy can be applied to a WAN Edge device. Both control and data policies are configured within this policy and prefix-lists are created within this policy. Route-policies, as-path lists, community-lists, qos-map policies and access lists will be included in this localized policy.
Configuring Centralized Policy
We need to consider three main components while configuring centralized policy in the vManage.
Lists - Lists are used to group related items, used when applying policy or used in matching or actions within the policy. Lists for applications, color, data prefixes, policers, prefixes, sites, SLA classes, TLOCs, and VPNs can be created.
Policy definition - There are different types of policy definitions:
- App-route policy - An application-aware routing policy can be created which tracks path characteristics such as loss, latency, and jitter. If there is a match of SLA categories with the traffic, the traffic is directed to the path based on the criterions matched with the SLA categories.
- Cflowd template – Cflowd template, which sends sampled network data flows to collectors.
- Control policy - Operates on the control plane traffic and influences the routing paths in the network.
- Data policy - Influences the flow of data traffic based on the fields in the IP packet header.
- VPN membership policy - Participation in VPNs on WAN Edge routers can be restricted and the population of their route tables.
Policy application - The policy is applied on which site list.
Routes and TLOC attributes are examined by Control policy and modifies attributes that match with the policy. The Policy is unidirectional and can be applied in an inbound or outbound direction to a site list. If applied in the inbound direction, then policy would affect routes coming from the sites and actions would be applied on the vSmart controller. But, if the policy is applied in the outbound direction, then the policy would affect routes moving towards the sites and actions will be applied to the sending vSmart controller.