The Autonomous System Number is assigned a globally unique 16-digit identification number known as the autonomous system number or ASN, by the IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority). The autonomous system number range is 1 to 65535. From 1 to 64511 are available by IANA for global use called public AS number. And the 64512 to 65535 series is reserved for private communication purposes more like private IP addresses.
A set of Internet-routable IP prefixes belonging to a network of an organization, controlled and supervised by a single AS Number called AS domain. An AS domain utilizes a common routing policy controlled by the organization.
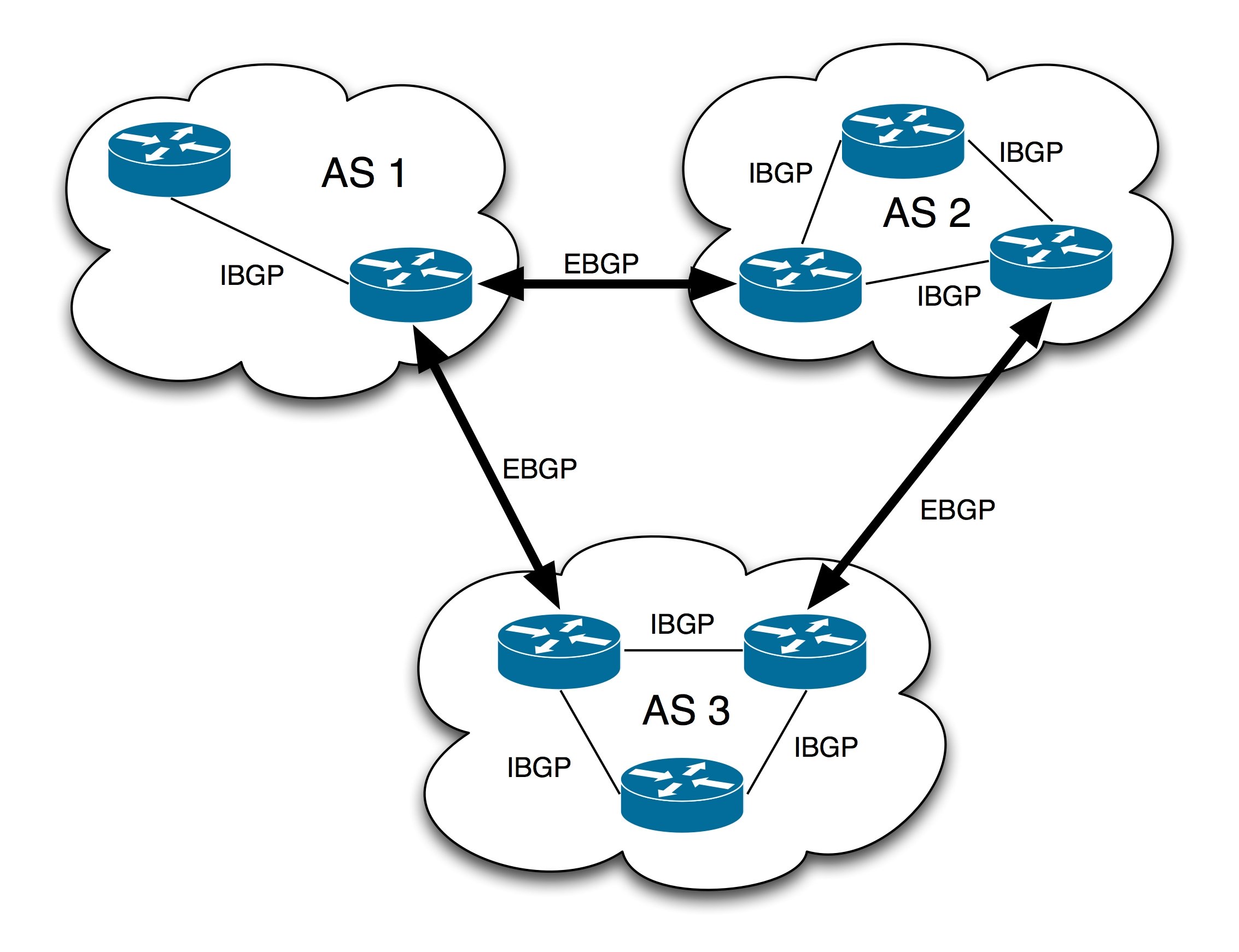
Autonomous Systems were introduced to regulate networking organizations such as Network operators or Internet Service Providers (ISP) to control routing within their networks and to exchange routing information with other Internet Service Providers, Educational Institutions and Government Organizations.
Just like public IP addresses, public ASNs (Autonomous System Numbers) have to be unique on the Internet. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the protocol that helps ASNs to be unique on the internet. BGP manages the routed peering, prefix advertisement, and routing of packets between different autonomous systems across the Internet. BGP uses the Autonomous System Numbers to uniquely identify each system. In effect, BGP is the routing protocol for AS paths across the Internet.